In today’s busy market, you can’t just sell to everyone the same way. Think about it: people are all different! They like different things, need different stuff, and act in different ways. To truly get noticed, businesses must deliver the perfect message to the perfect audience at the perfect moment. This is exactly what Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) helps you do.
Table of Contents
What is the STP Model?

The STP model is a super popular and effective way to market your business. It’s a smart approach that helps brands:
Focus their marketing: Instead of wasting money trying to reach everyone with the same message, Segmentation Targeting and Positioning (STP) helps you aim your efforts at the people who are most likely to buy from you. That means your marketing budget works harder.
Connect better with customers: When your message feels like it’s made just for them, customers pay more attention. They feel understood and more connected to your brand, which is a direct benefit of effective Segmentation Targeting and Positioning (STP).
Ultimately sell more: Happy, engaged customers who feel like you get them are much more likely to choose your products or services, a key outcome of successful Segmentation Targeting and Positioning (STP).
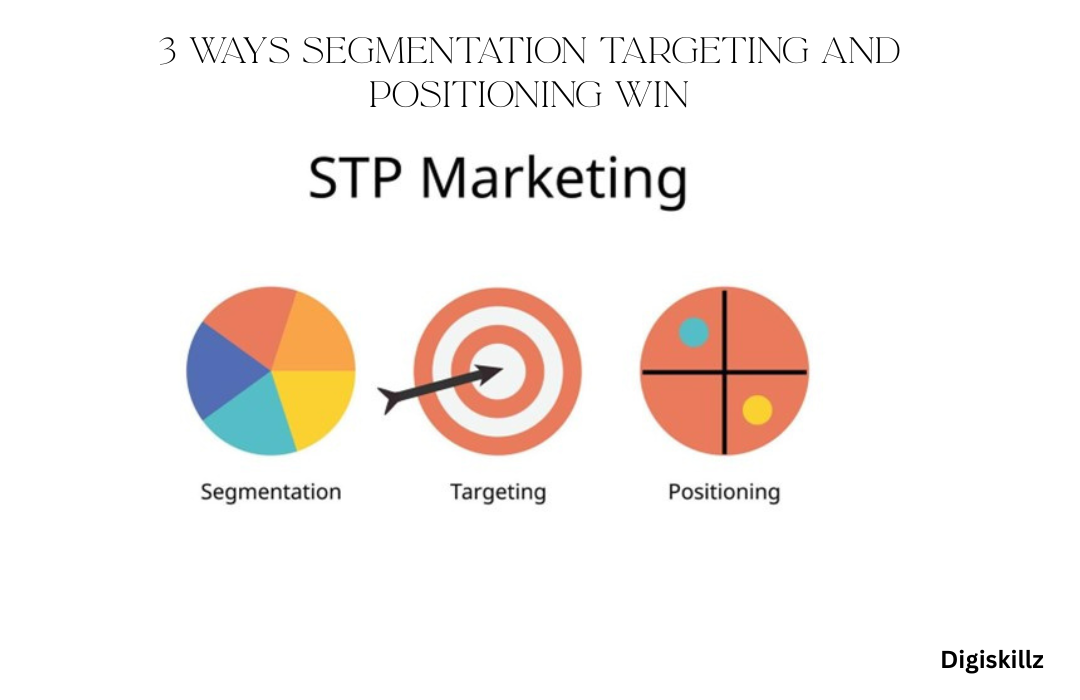
In this guide, we’ll break down each part of segmentation targeting and positioning (STP): Segmentation (splitting customers into groups) Targeting (picking which groups to focus on) and Positioning (how you want customers to see your brand). You’ll learn how businesses can use this simple yet powerful model to get ahead.
What Does STP Mean in Marketing?

STP stands for Segmentation Targeting and Positioning. It’s a three-step plan that helps marketers find their most valuable customer groups, reach them with special marketing messages, and present their products or services in a way that truly connects with those groups.
Let’s look at each step:
-
Market Segmentation: Understanding Your Audience
What is Segmentation? As the first step in segmentation targeting and positioning, market segmentation is like sorting a huge pile of toys into smaller, more organized bins based on what they have in common (like all the cars in one bin, all the dolls in another). In business, it means taking a big group of customers or other businesses and splitting them into smaller, easier-to-manage groups based on shared features. This helps marketers make smarter plans and stop wasting money on general ads that don’t connect with anyone.
Types of Segmentation: As the first step in segmentation targeting and positioning, there are four main ways to split up your market:
Demographic Segmentation: This is about basic facts about people.
Based on: Age, gender, income, education, job, family size, etc.
Example: A fancy car brand might aim its ads at people who earn a lot of money.
Geographic Segmentation: This is about where people live.
Based on: City, region, country, climate, etc.
Example: A company selling warm winter coats would focus its marketing in colder areas.
Psychographic Segmentation: This looks at people’s inner qualities.
Based on: Personality, values, interests, hobbies, lifestyle (e.g., are they adventurous, health-focused, artistic?).
Example: Brands that care about the environment often target customers who strongly believe in sustainability.
Behavioral Segmentation: This is about how people act.
Based on: What they buy, how often they buy, how loyal they are to a brand, how they use a product.
Example: Netflix might suggest different shows to you based on what you’ve watched before.
Why Segmentation Matters Splitting your market into segments is super helpful because it:
You can build better products that genuinely solve particular problems for customers.
You’re able to send custom messages that genuinely connect with different customer groups.
Gets you more for your money by focusing on customers who are likely to bring in more business.
2.Targeting: Choosing the Right Group

What is Targeting? After you’ve sorted your customers into groups (segments), the next step in segmentation targeting and positioning is targeting. You’ll then assess these customer groups to identify those with the highest potential for your brand. You can’t be everything to everyone!
Targeting Strategies There are a few ways to choose which groups to target:
- Undifferentiated Targeting (Mass Marketing): This is when you treat the whole market as one big group.
Example: Basic everyday items like salt or sugar – everyone needs them, so the marketing is usually general.
- Differentiated Targeting (Segmented Marketing): This is when you pick a few different groups and send different messages to each one.
Example: A car company might sell family SUVs to parents and sleek sports cars to young professionals, with different ads for each.
- Concentrated Targeting (Niche Marketing): This is when you focus all your efforts on just one very specific group.
Example: A brand that only sells vegan protein shakes might focus solely on vegan athletes.
- Micromarketing (Local or Individual Marketing): This is super specific, tailoring your marketing to individual customers or very small local areas.
Example: A coffee shop might offer different drink specials based on what people in that specific neighborhood prefer.
Things to Think About When Targeting When picking your target groups, consider:
How big is the group, and can it grow?
How much competition is there in that group?
Do your company’s goals and resources fit with that group?
Can you easily reach and communicate with this group?
Benefits of Targeting Smart targeting helps you:
Avoid spending marketing money on uninterested audiences.
Attract and keep more customers.
Create more focused and convincing ad campaigns.
3. Positioning: Crafting the Right Message
What is Positioning? As the final stage in segmentation targeting and positioning, positioning is what makes your brand stand out and how people think about your brand compared to your rivals. It’s the step where you create a clear image and special value for your chosen audience. It highlights how you’re unique and superior in the eyes of your target customers.
What is a Positioning Statement? A clear positioning statement helps you define:
Who your product is for (your target group).
What your product does (its main be What is Positioning? As the final stage in segmentation targeting and positioning, positioning is what makes your brand stand out and how people think about your brand compared to your rivals. It’s the step where you create a clear image and special value for your chosen audience. It highlights how you’re unique and superior in the eyes of your target customers.nefit).
Why it’s better than other choices (what makes it special).
Example Positioning Statement: This statement demonstrates effective segmentation targeting and positioning: “For environmentally conscious travelers (target), Eco Go Travel offers sustainable vacation packages (benefit), unlike traditional travel agencies that contribute to over-tourism (what makes it different).
Tools for Good Positioning
- Perceptual Maps: These are visual charts that show how customers see different brands based on important features (e.g., price vs. quality).
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): This is your clear, compelling reason why a customer should pick your product over everyone else’s.
- Brand Messaging: This includes everything from your slogans, the way you talk, your visuals, and your content – all designed to strengthen how people see your brand.
Examples of Good Positioning
Apple: Known as a premium, stylish, and user-friendly tech brand.
Nike: Positions itself around power, athletic greatness, and the idea of “Just Do It.”
Volvo: Famous for safety and reliability.
The STP Process in Action: Real-World Example (Nike)

Nike provides a great real-world example of how segmentation targeting and positioning operates.
- Segmentation: Nike divides its market based on things like age, gender, lifestyle (e.g., active vs. casual), and how much they exercise or which sports they play.
- Targeting: Nike aims at many different groups, including young athletes, people who love fitness, and even fashion-conscious individuals. They use different messages for each group.
- Positioning: Nike wants people to see it as a brand that inspires and helps athletes achieve their best through new ideas and top performance. Their famous slogan, “Just Do It,” embodies this perfectly.
Why STP is Super Important in Digital Marketing

With so much happening online, making things personal and focusing on the customer is more vital than ever. STP is key for digital marketing because it helps with:
- Email Campaigns: Sending emails to specific groups means your messages are more personal and lead to more sales.
- Social Media Ads: Aiming ads at specific ages, interests, or locations makes your ads work much better.
- Content Marketing: Creating blog posts, videos, or articles that speak directly to each customer group makes them more engaged.
SEO & PPC (Search Engine Optimization & Pay-Per-Click ads): Using the right keywords for each group helps your business show up higher in search results and gets you more for your ad money.
Challenges When Using STP

Even though STP is powerful, it can have some tricky parts:
- Gathering and understanding data can take a lot of time.
- Splitting the market into too many tiny groups might spread your resources too thin.
- People’s behaviors change, so you need to constantly update your groups and plans.
- Getting your positioning wrong can confuse customers and make them lose trust in your brand.
Tips for a Winning STP Strategy

To make your Segmentation and Targeting And Positioning (STP) strategy a success:
- Use real data: Look at information from your customer records, website analytics, and customer feedback.
- Review your groups regularly: Markets change, so check if your segments still make sense.
- Test your messages: Try out different positioning ideas with small groups before launching big campaigns.
- Match STP with your overall business goals: Make sure your marketing strategy helps your business grow in the right direction.
Segmentation Targeting and Positioning are the backbone of any good marketing plan. When done right, STP helps businesses understand their customers better, use their money more wisely, and build stronger, more meaningful relationships with the people they want to reach.
With so many ads competing for attention, the real power lies in speaking precisely and effectively to the people who matter most. And that’s exactly what segmentation targeting and positioning (STP) helps you do.
In today’s fast-moving digital world, businesses can’t afford to speak to everyone the same way. Because customers are distinct, they naturally have varying needs, preferences, and behaviors. That’s why Segmentation Targeting and Positioning (STP) is such a powerful strategy. It helps brands focus their efforts, deliver tailored messages, and build stronger relationships with the right audience.
The Segmentation Targeting and Positioning (STP) model offers immense power. Segmentation allows marketers to divide the market into smaller groups with similar traits. Targeting helps them choose the most valuable groups to focus on. Positioning shapes how a brand is perceived by those chosen audiences. When all three steps work together, marketing becomes more efficient, impactful, and personal.
Brands like Nike, Apple, and Volvo effectively use segmentation targeting and positioning (STP) to craft messages that resonate deeply with their ideal customers. Whether it’s through email campaigns, social media ads, blog posts, or search engine strategies, STP helps make every piece of marketing more relevant and more likely to drive results.
However, successful segmentation targeting and positioning (STP) requires effort. It demands good data, constant updates, and a clear understanding of what makes your brand special. When done right, though, it leads to smarter spending, greater customer loyalty, and higher sales.
In a crowded market, the real advantage isn’t volume, but intelligence in your communication. And that’s exactly what segmentation targeting and positioning (STP) helps you achieve. By understanding who your customers are, what they want, and how to connect with them, you set your brand up for long-term success.
So, don’t try to reach everyone. Focus on reaching the right ones—and do it in a way that truly speaks to them. That’s the real power of Segmentation Targeting and Positioning.
Author:Nishmidha
Learner of DigiSkillz, Digital Marketing Institute in Kochi.









Leave A Comment